In today’s digital world, the growing number of online customers and shifting business environment have pushed companies to differentiate themselves in their e-commerce offerings by providing better services and customer experience. It is in this context that chatbots have become so integral to online retail businesses that customers can sometimes struggle to discern whether they are being assisted by a person or a well-programmed chatbot[1].
If you are a regular customer of any online e-commerce platform and have had to chat with customer support for any issue like requesting a refund, chances are, you were conversing with a chatbot.
The need for chatbots rose sharply due to the global pandemic, which led to increased adoption of e-commerce by both retailers and customers. In the U.S., online shopping during the 2020 holidays grew by 32.2% compared to 2019[2]. In that November alone, Black Friday and Cyber Monday catapulted e-commerce sales to over $100 billion[2]. In such a high-volume context, it became more viable to invest in chatbots to take over the first layer of consumer communication for many functions and queries.
Rising relevance of chatbots in e-commerce
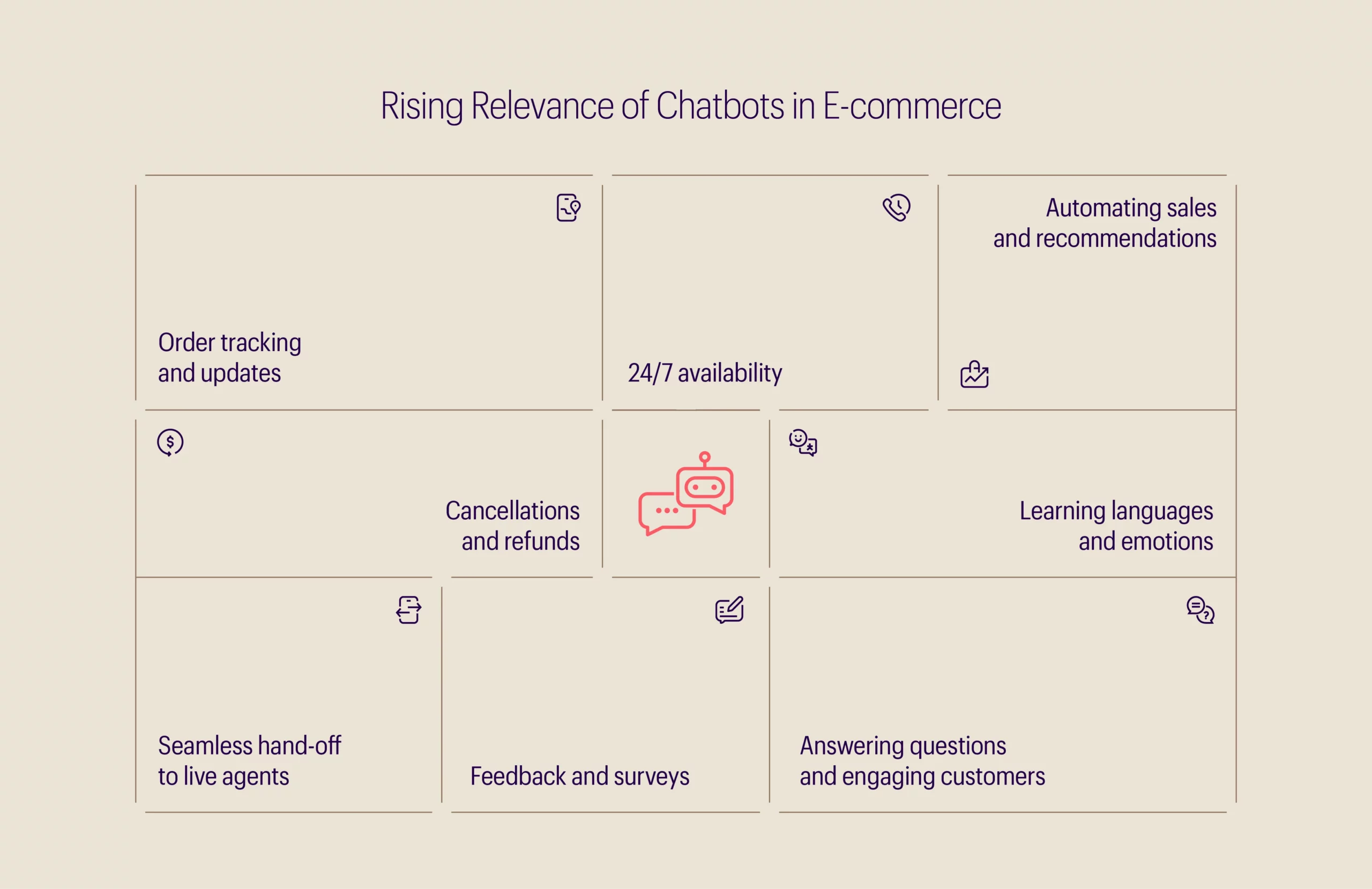
In today’s post-pandemic context, despite the economy reopening with a relative return to normalcy, the value of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) has remained substantial, especially in the retail industry, which finds itself striving for personalized and customizable customer experiences both in-store and through websites and applications without the need for manual human labor at every step. Chatbots, in this regard, have become integral components of e-commerce functions, taking over basic assistance and questions and post-order queries such as order cancellations, refunds, and delivery tracking, essentially taking over tedious interactions and repetitive responses while human employees can focus on more important functions and those handed over to them by the chatbot. A Gartner survey found that 54% of customer service and support (CSS) systems utilized some form of chatbot, virtual customer assistant (VCA), or conversational AI platform for customer-facing applications[3].
As a result of the global shift to online services, consumers may have had no choice but to familiarize themselves with the digital aspects of engaging with retailers. However, the necessity of online interaction with vendors and retailers, combined with people’s increasing familiarity with technology, led to chatbots eventually being not only well-received but often preferred by many people. For instance, a 2021 report found that around 55% of U.S. consumers preferred to use a chatbot over waiting for a human agent[4].
Chatbots are predicted to become even more prevalent as their quality and people’s familiarity with them increases. The global chatbot market reached a value of $3.7 Billion in 2021-2022 and is expected to reach $13.9 Billion by 2027, exhibiting a CAGR of 24.68% during 2021-2027[5].
How chatbots empower online retailers
We are at a point where the potential of chatbots is starting to be realized. What once were shipping update notifiers and FAQ answering machines are now slowly becoming an important asset in e-commerce through the following ways:
1. Going beyond predefined FAQs:
Chatbots now handle answering frequently asked questions (FAQs) easily, and the predefined answer method of handling FAQs works to a reasonable extent[6]. However, such systems pale in comparison to those built with natural language understanding (NLU), which can handle both predefined questions as well as understand questions that are not in the playbook reasonably well. Perhaps the most important aspect of this is that NLU-powered chatbots continuously develop their language inventory, constantly expanding their own capabilities. Though NLU-powered chatbots take more effort and time to set up, their capabilities go beyond vocabulary building and include language identification, spell checking, detecting convenient conversation triggers, and retaining context after conversations. Advancements in natural language learning directly contribute to why chatbots today feel more human and can respond to a wider variation of responses. Additionally, chatbots also empower live agents and customer support teams by automating first responses and resolving less complicated issues such as order cancellations, tracking updates, and other post-order queries.
2. First layer of contact:
One of the main reasons why people often prefer interacting with a chatbot over a human agent is that for what information they can provide and queries they can answer, they do so quickly and consistently[8]. They also have the advantage of 24/7 availability. These factors place chatbots in a great position to become the consumer’s first layer of contact with a retailer or vendor. For example, chatbots can pick up on when a user seems to be stuck in one section of the website and trigger a conversation to offer help; recognize a returning customer and recall the context of their previous shopping to personalize recommendations for that visit; and collect immediate feedback on their services.
3. Scalability through customizability:
Chatbots and conversational AI, like any other technology, require customization over time. Customization includes both effective integration and creating a unique customer experience[6]. For example, customers of an e-commerce website may be able to generate app or purchase analysis reports for a user account; a chatbot could clarify parts of the report on request while simultaneously collecting information on which parts of the report are most frequently confusing. Well-integrated chatbot use cases such as the above example would also ease data collection if the e-commerce website were to scale up and must deal with increasing amounts of data.
4. Also for internal use:
Retailers who are using chatbots can not only benefit from using them for consumers but also deploy them internally for their employees. Just like consumers, employees also struggle to get answers on a wide range of topics and issues across multiple departments[7]. These include holiday dates, obtaining documents such as verification letters, reservation of office spaces, and vendor relations questions, just to name a few. Having to talk to the right people for matters like these could result in inefficiency and frustration for all involved. Chatbots can be virtual agents for connecting the right people with the right queries, and for accessing and automating HR functions, etc.
Challenges with widespread adoption
While chatbots have advanced considerably over recent years, there are still key areas of concern regarding their continued and widespread adoption for e-commerce. Despite the increasing acceptance of chatbots, as mentioned previously, there is also evidence to highlight that human interaction still has an important place in customer service. A separate study found that 82% of US shoppers and 75% of international shoppers want more human interaction[9]. As retailers continue developing their digital strategy, they also need to balance automated assistance with human interaction. Relying too heavily on automation can provide an impersonal or even frustrating customer experience. Intelligent chatbots tasked with the right kind and volume of work and set to answer the right questions can free up human agents’ time as well as connect them to the right customers frictionlessly.
Additionally, in the war for data privacy and protection, well-intentioned initiatives and platforms often get caught in the crossfire, leading to a loss of both revenue and public trust[10][11]. Data collection today goes beyond just databasing names, addresses, and credit card information; but also purchase history, location, and shopping behavior, to name a few [12]. Consumers could have concerns about their privacy and the safety of their personal information. To consumers, AI-driven chatbots might feel like leaking ships that are hoarding huge amounts of personal data every time they interact with them. Ultimately, data privacy is likely to always be a concern, and it is up to retail vendors to make sure they have robust safety and governance mechanisms in place that instill trust in consumers.
Conclusion
Chatbots have come a long way from being simple predefined answering machines. They are now an invaluable tool for retailers, capable of being the first point of contact for not only customers but even employees; freeing valuable time by handling the simpler side of customer service while also having the potential for exponential growth through machine learning and data collection. While they are not an answer to all the problems of e-commerce, they hold incredible potential to revolutionize the way we buy and sell online in the future.
This is the first in a series of articles on developments in e-commerce and online retail. Check out our other articles in the series to know how social media and the metaverse are changing e-commerce.
Interested in learning more about customer support automation? Read our interview with Mathco’s Head of Innovation, Sourav Banerjee, on this topic.
Bibliography
1. Chen, Ja-Shen, Tran-Thien-Y Le, and Devina Florence. “Usability and Responsiveness of Artificial Intelligence Chatbot on Online Customer Experience in E-Retailing.” International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, May 7, 2021. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJRDM-08-2020-0312/full/html.
2. Grohs, Bob. “Covid-19 Has given Rise to Mass Chatbot Adoption.” Total Retail, October 25, 2021. https://www.mytotalretail.com/article/covid-19-has-given-rise-to-mass-chatbot-adoption-in-the-retail-space/.
3. Conn, STAMFORD. “Gartner Predicts Chatbots Will Become a Primary Customer Service Channel within Five Years.” Gartner, July 27, 2022. https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2022-07-27-gartner-predicts-chatbots-will-become-a-primary-customer-service-channel-within-five-years.
4. Britt, Phil. “5 Customer Experience Chatbots Benefits.” CMSWire.com, October 20, 2021. https://www.cmswire.com/customer-experience/5-benefits-that-chatbots-can-bring-to-your-customer-experience/.
5. ltd, Research and Markets. “Chatbot Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2022-2027.” Research and Markets – Market Research Reports – Welcome, July 2022. https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5633297/chatbot-market-global-industry-trends-share?utm_source=BW&utm_medium=PressRelease&utm_code=hmlrtf&utm_campaign=1739208%2B-%2B%2413.9%2BBillion%2BWorldwide%2BChatbot%2BIndustry%2Bto%2B2027%2B-%2BFeaturing%2BCreative%2BVirtual%2C%2BeGain%2Band%2BVerint%2BSystems%2BAmong%2BOthers&utm_exec=jamu273prd.
6. Botpress. “Ultimate Guide to Chatbots.” Ebook – Ultimate Guide to Chatbots, 2022. https://f.hubspotusercontent20.net/hubfs/20692578/BPS102%20E-book%20Ultimate%20Guide%20to%20Chatbots%20AW.pdf.
7. Sethi, Rajeev. “ServiceNow Brandvoice: Chatbots: Not Just for Customers Anymore.” Forbes, November 5, 2021. https://www.forbes.com/sites/servicenow/2021/11/05/chatbots-not-just-for-customers-anymore/?sh=62bcd1830991.
8. Tran, Anh D., Jason Pallant, and Lester W. Johnson. “Exploring the Impact of Chatbots on Consumer Sentiment and Expectations in Retail.” Exploring the impact of Chatbots on consumer sentiment and expectations in Retail, November 2021. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354047226_Exploring_the_impact_of_chatbots_on_consumer_sentiment_and_expectations_in_retail.
9. Noonan, Joseph. “Council Post: Ideal Online Shopping Experiences Require Balancing Automation with a Human Touch.” Forbes, October 18, 2021. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2021/10/18/ideal-online-shopping-experiences-require-balancing-automation-with-a-human-touch/?sh=7175ac0e3003.
10. Wong, Karen. “Survey: HK Folks Stop Shopping Online Due to Data Privacy Concerns.” Marketing, September 9, 2022. https://www.marketing-interactive.com/hk-consumers-online-data-privacy.
11. Asher-Schapiro, Avi, and David Sherfinski. “Analysis: Chatbots in U.S. Justice System Raise Bias, Privacy Concerns.” Reuters, May 10, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/legal/litigation/chatbots-us-justice-system-raise-bias-privacy-concerns-2022-05-10/.
12. Avidon, Eric. “Data Privacy Concerns Grow as Legislation Lags: TechTarget.” Business Analytics, September 14, 2022. https://www.techtarget.com/searchbusinessanalytics/news/252524960/Data-privacy-concerns-grow-as-legislation-lags.


