The landscape of procurement is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the increasing complexity of global supply chains. Organizations must adapt to remain competitive, addressing critical challenges that impact efficiency, accuracy, and strategic alignment. The future of procurement hinges on leveraging innovative solutions to overcome these hurdles and enhance overall performance.
This article explores the pivotal role of data analytics and Gen AI in shaping the future of procurement, highlighting key challenges faced by organizations and the transformative solutions offered by MathCo.
Why is There a Need to Build a Robust Procurement Foundation?
Organizations often face significant challenges in procurement, hindering efficiency, accuracy, and strategic alignment. Common issues include unreliable data governance, mismatched data taxonomies, reconciliation problems, and a lack of centralized access to information. Inefficiencies like redundant reports, delays caused by manual processes, and the high occurrence of manual contract reviews are common. Additionally, procurement functions often suffer from reactive insights and inadequate predictive capabilities. They face poor integration with business processes, underutilized disparate solutions, limited visibility into supplier performance, and difficulties in compliance and auditing.
Scalability issues, challenges in technology adoption and user experience, and risk management further complicate the procurement landscape. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach that integrates technology, process improvements, and alignment with the business goals. By doing so, organizations can enhance their procurement functions and remain agile and efficient.
Key Challenges in the Procurement Value Chain
Organizations encounter several critical challenges within their procurement functions, such as fragmented data spread across various systems, making it hard to get a comprehensive view of procurement activities. This fragmentation leads to inefficiencies, missed opportunities for cost savings, compliance issues, and increased risk exposure. Additionally, the lack of standardized processes and data structures complicates the accessibility to prompt and actionable insights.
Several areas within procurement face significant challenges:
- Data Management and Quality: Common challenges include category mismatches, lack of standard taxonomies, data duplication, redundancy management, and handling unstructured data and metadata development.
- Analytics and Insights: A high degree of manual processes and the generation of reactive rather than proactive insights hinder efficiency.
- Adoption: The abundance of solutions and tools, along with misaligned integration with business processes, and the lack of standardized reporting and consumption methods, add complexity to procurement operations.
These challenges collectively limit the overall efficiency of the team, increasing the risk and cost associated with the procurement function.
MathCo’s effective procurement strategy
MathCo’s hybrid approach brings together the right skill sets and an advanced analytics toolkit to power enterprises with a supercharged brain. To enhance procurement impact metrics, we set up a successful procurement strategy based on four foundational pillars to deliver true value and impact:
- Data Foundation
- Data Science and Analytics
- Business Insights and Reporting
- Adoption
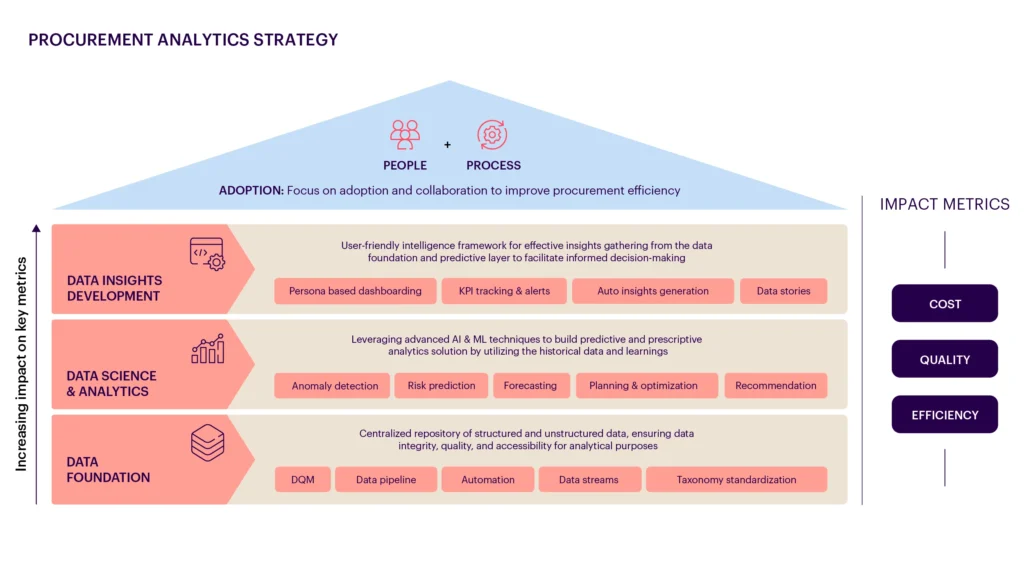
Data Foundation
To future-proof procurement, it is crucial to establish a robust data foundation for high-quality, standardized data accessibility and trust. A key component of this process is constructing a semantic layer that captures data aligned with key performance indicators (KPIs) and business requirements. This layer should provide ready-to-use data tailored to procurement insights and decision-making needs. Consolidating data from various procurement systems and tools, including both structured and unstructured data, enriches overall intelligence.
Moreover, implementing a framework with standard data treatments is essential for processing complex data such as contracts, invoices, bills, and ERP system data. This ensures data consistency and accuracy, thereby improving efficiency and quality. Additionally, setting up a standardized data quality framework is critical for maintaining data consistency and monitoring performance for ongoing review.
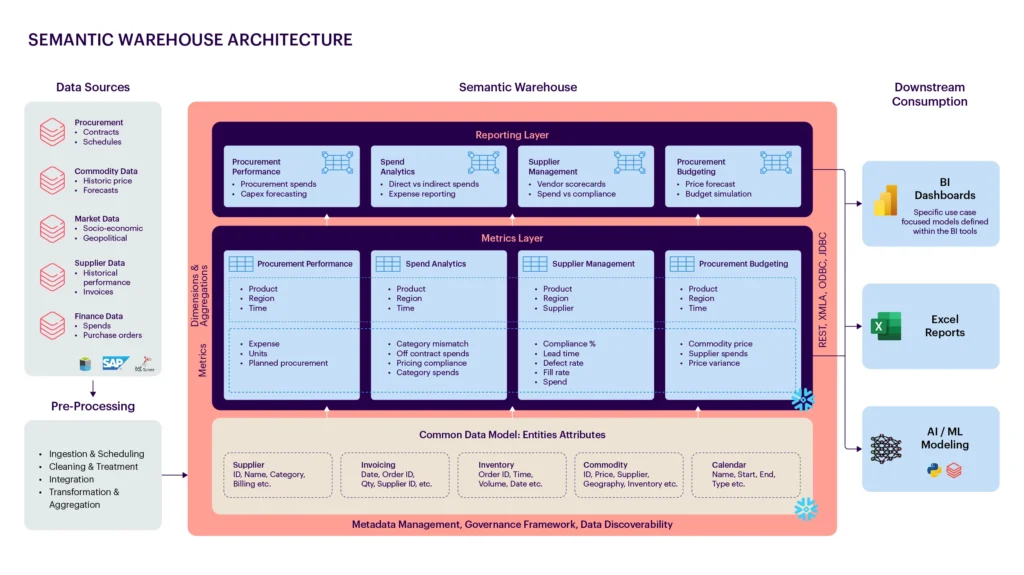
Data Science and Insights
Assessing the current state of procurement intelligence, solutions, and processes is crucial for identifying the most impactful analytics use cases to enhance procurement functionality. The proposed framework aids in pinpointing quick wins that the procurement team can leverage based on their analytic maturity and the business value for the organization. Further details can be found in the figure below.
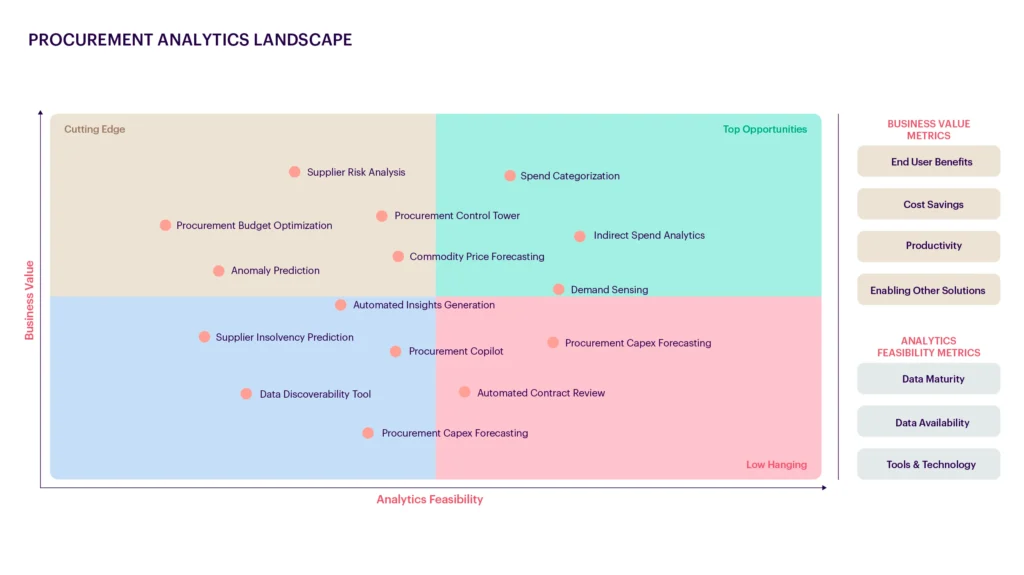
Ensuring that solutions are explainable and contextualized is essential for improving their usability and overall adoption of the solutions. This approach fosters a deeper understanding and more effective integration of the solutions developed for procurement.
Foundational Intelligence: Handling unstructured data using NLP and GenAI enhances the procurement data foundation by extracting metadata, measuring contract compliance, and gathering market trends and reports through data scraping and extraction. This facilitates building spend categorization, indirect spend analysis, and automated spend mismatch analysis and resolution to reduce costs and improve data consistency.
Building Predictive and Prescriptive Intelligence: Solutions such as supplier risk assessment, anomaly detection, commodity price forecasting, and procurement budget planning and simulation capabilities enable procurement teams to make more efficient business decisions and reduce costs.
Advanced GenAI Solutions for Improved Efficiency and Consumption: Features such as copilot capabilities for better planning and decision-making, automated insights generation for improved insights consumption, standardized reporting, and contract risk assessment to reduce supplier compliance risk improve the day-to-day experience and efficiency of procurement teams.
Business Intelligence Reporting: This plays a crucial role in user onboarding, as it facilitates the seamless transition of users into a new system or platform. It also significantly affects adoption and usage rates by providing clear, actionable insights that are easily accessible. When users can intuitively navigate and use BI tools, they are more likely to engage with the system regularly, thereby maximizing the value derived from data-driven strategies. By prioritizing user-centric design in BI reporting, organizations can enhance user satisfaction and promote continuous engagement.
With our extensive experience in building customer-centric solutions, we have identified several core consumption principles that ensure effective BI reporting:
- Designing solutions around existing infrastructure ensures technological self-sufficiency and seamless integration.
- A user-centric design approach caters to the distinct needs of key and critical users.
- Design sequencing breaks complex services into manageable user journey sections.
- Hyper-automation enables seamless business and insights monitoring.
Incorporating innovative features like customized alerts, notifications, user governance and control, GenAI functionalities for enhanced consumption, and downstream applications such as automated summaries and PPT generation fosters innovation and improves overall efficiency.
Adoption
Adoption of systems and solutions is a significant challenge for many organizations. Despite substantial investments in advanced tools and technologies, they often struggle to achieve widespread usage. One key reason is the entrenched preference for legacy platforms and the reliance on individual knowledge and established processes. These familiar methods feel more comfortable and reliable to users, creating resistance to change. Additionally, if new solutions are not designed with the end-user in mind or fail to demonstrate immediate value, they can be perceived as cumbersome or unnecessary. This disconnect can lead to underutilization of even the most sophisticated systems.
To improve adoption, we must ensure there are a few basic principles covered:
- Enable user collaboration across business units
- Solution development and customization based on user personas to ensure consumption
- Defining data standards and reporting standards based on the users and business decisions
- Enabling change management and socialization of developed solutions through workshops, building a brand for the solutions, user interviews, and user collaboration during development to ensure adoption.
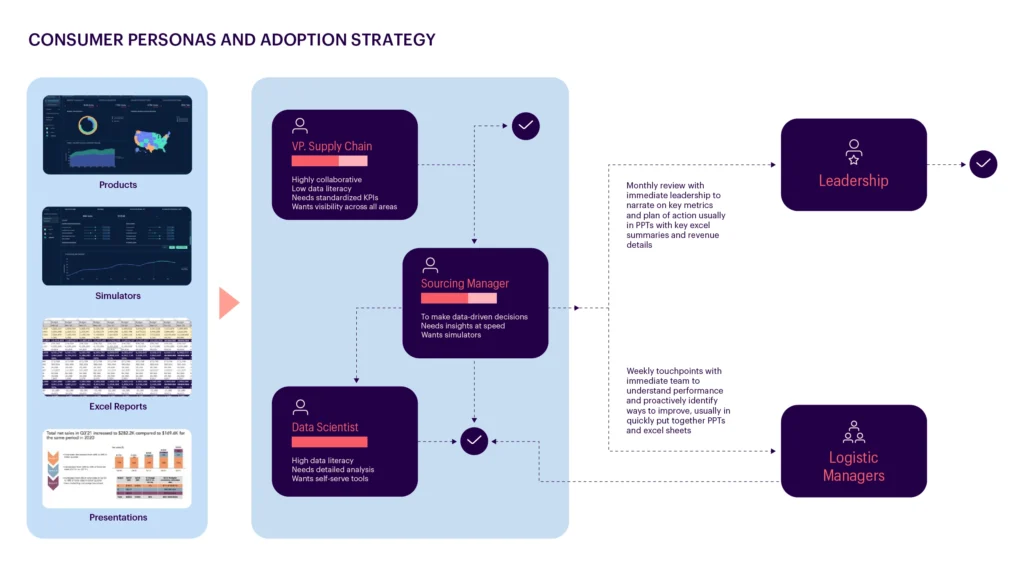
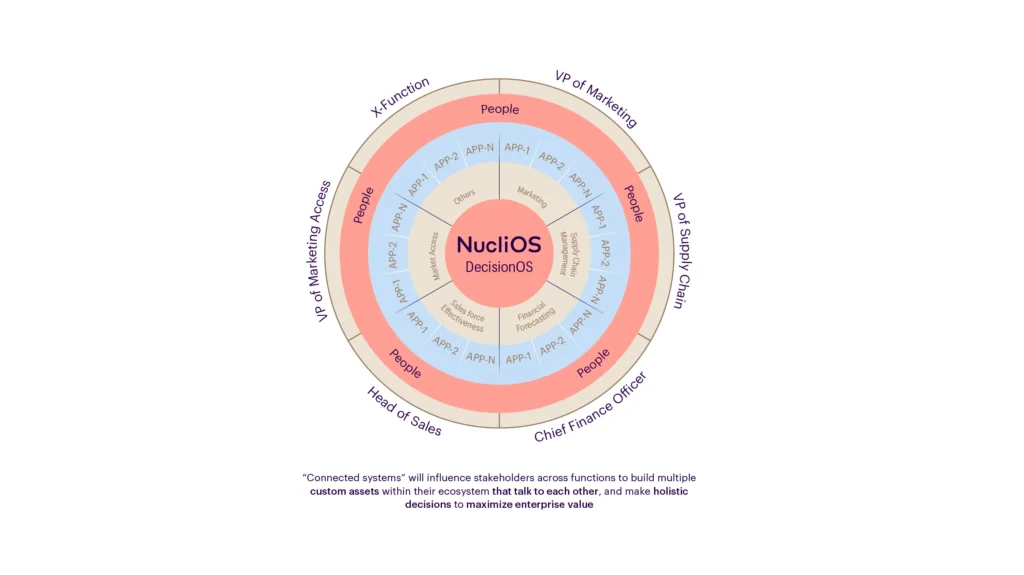
Bringing it All Together with a Connected Ecosystem
Integrating data, intelligence, and advanced analytics into a connected ecosystem ensures a cohesive and efficient procurement process. Acting as a central nervous system, this ecosystem seamlessly connects data, analytics, and user adoption. This integration streamlines the procurement process, allowing information to flow freely between analysis tools and users, ensuring everyone has the necessary information.
Businesses can set up their processes for crucial decisions, such as planning procurement cycles, selecting suppliers, and planning budgets. To support these decisions, stakeholders need to leverage various tools and analyses to arrive at effective conclusions. Connected systems provide a unified platform where data, analytics, and insights converge, enabling well-informed decision-making. This integrated approach enhances decision-making and optimizes procurement operations for efficiency and effectiveness.